Nonfunctional Requirements Explained: Examples, Types, Tools
What are non-functional requirements?
Non-functional requirements (NFRs) are specifications of a system that determine its performance and quality while it is in use. NFRs address how the system behaves under various conditions rather than what the system does. These include aspects like performance, security, usability, reliability, and scalability.
For instance, a non-functional requirement about a car might be that “interior cabin noise of the automobile must not exceed 70 decibels at highway speeds (60 mph or 97 km/h) under standard operating conditions.”

- Arunabh Satpathy
- June 21, 2024
- 16 minutes
Non-functional requirements usually contrasted with functional requirements, which talk about what a system does instead of its specific performance and qualities. A functional requirement for a car might be, “The car must accelerate from 0 to 60 mph within 10 seconds.”
Non-functional requirements describe how well a system functions. They create the basis for how a system feels. Most modern companies using application lifecycle management tools like Jira or Azure DevOps use NFRs these days. They’re also turning to new methodologies like Agile and BABOK to adapt to the changing market.
Both types of requirements are important to successfully develop and launch a product or system. This article covers non-functional requirements, how they work, different types, deployment within Azure DevOps, and the differences between functional and non-functional requirements.
Table of Contents
Get a personalized demo and find an efficient way to
Improve Your Requirements
Lifecycle Significantly
Get a personalized demo and find an efficient way to
Improve Your Requirements
Lifecycle Significantly

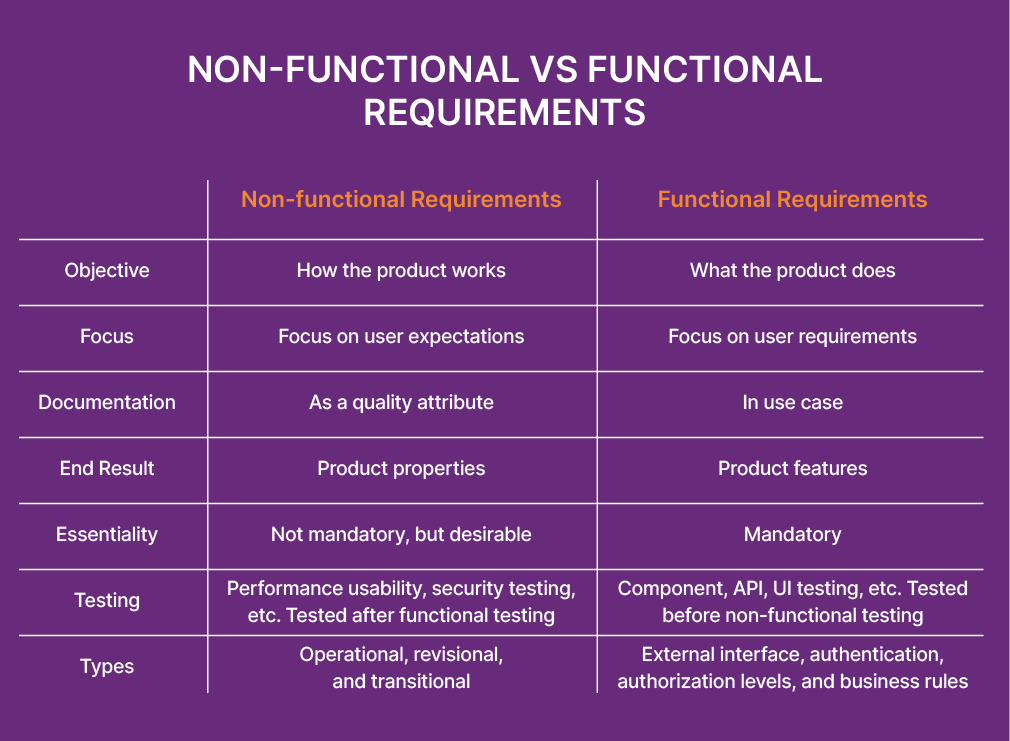
1. Difference between Functional and Non-functional Requirements
The differences between a functional and non-functional requirement can be confusing. But understanding the differences can help you write great requirements for your project. The traditional comparison between functional and non-functional requirements is as follows:
- Functional requirements are the actions a system must perform. They describe what the system should do.
- Non-functional requirements define how the system performs the actions. They describe how well the system should do something.
- Both types are essential parts of a well-defined requirements management strategy.
i. What are Functional Requirements? Is There an Example?
Functional requirements are requirements that define product features or functions that allow users to accomplish their tasks on a system. They are often simple to define, measure, and test. They are also less abstract than NFRs and generate very little confusion. If you asked someone to write a requirement, they would more likely create a functional requirement.
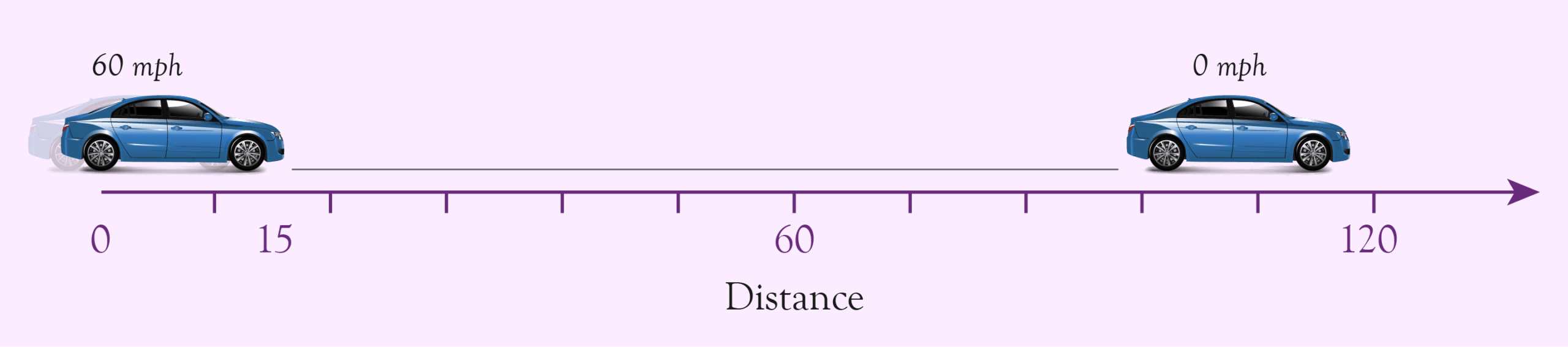
A functional requirement of a car sensor might be that the car should be able to stop from 60 miles per hour within 120 feet.
ii. What is a Non-functional requirement? Can You Give an example?
Non-functional requirements are the criteria that judge how well a system performs its functions. For example, a mobile website might have an NFR that says, “The system should load a webpage within 3 seconds.” This is a non-functional requirement that specifically defines the performance of the website.
NFRs are usually harder to define, measure, test, and track. Because of this, teams may end up using only functional requirements or constantly re-evaluate their non-functional requirements for correctness.
The downside of ignoring NFRs is that any team that doesn’t explicitly define them will struggle to meet its objectives. This is because NFRs act as the descriptor of success for a project, process, or system.
If you have a functional requirement that a car must have headlights that illuminate the road, you need a corresponding NFR that specifies how they achieve the goal of illumination.
For instance, an NFR for a car could say that its headlights should have a brightness of at least 10,000 lumens. This requirement adds meaning to the function of the headlights (i.e., illuminating the road) by describing the brightness level of headlights.
Without a list of NFRs about the headlight, engineers would have to guess at a number of attributes of a headlight:
- How bright are they?
- How long do they last?
- Are they fog resistant?
- Are they illegally bright or dim?
This is why NFRs are an important factor enhancing the overall user story. In our experience, they can even help maintain compliance.
2. What are the different types of nonfunctional requirements?
Now that we have understood what NFRs are and their differences from functional requirements, we need to talk about the different categories. There are various ways of understanding the types of non-functional requirements.
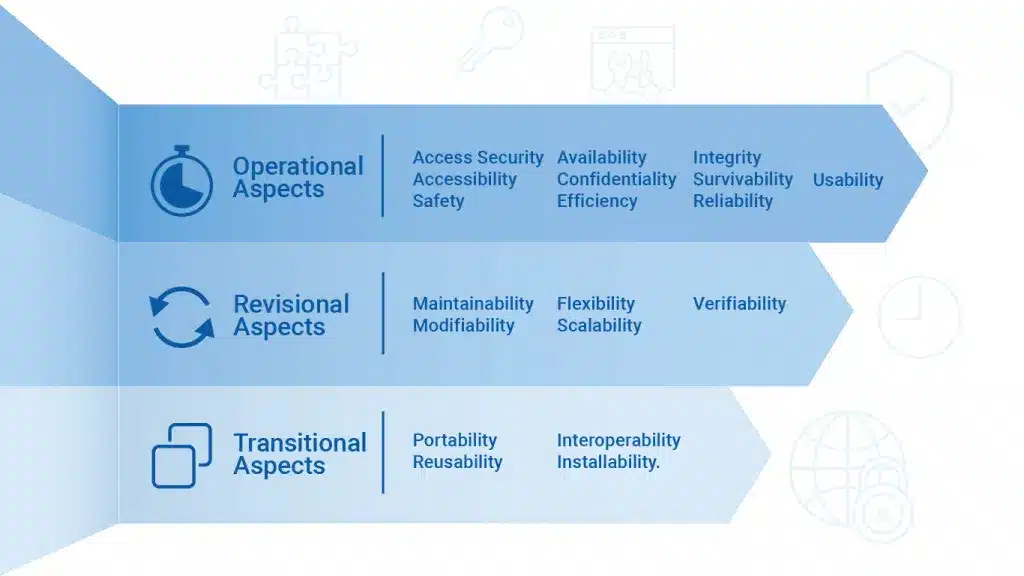
i. Operational, Revisional, and Transitional Aspects
Aspects of a system like scalability, durability, and reliability offer dozens of ways to group requirements. You don’t have to take each category during the development of a product, system, or process into account.
You can group non-functional requirements into three large categories or aspects:
1, Operational Aspects: These aspects focus on ensuring that the system functions effectively and securely under normal operating conditions.
2, Revisional Aspects: These ensure that the system can adapt to changing requirements and environments with minimal effort.
3. Transitional Aspects: These concern the system’s ability to transition smoothly from one state to another, such as integrating with other systems, migrating data, and adapting to changes in technology or business processes.
By covering every category and all aspects of each category, you can build non-functional requirements that give a goal for the system, process, and/or products that your team is involved with creating.
Let’s look at two examples of aspects that teams address when categorizing their non-functional requirements:
Scalability
Scalability is a revisional aspect of a piece of software, product, or process.
It refers to the ability of a product to scale (either up or down) to meet the usage demands imposed by its user base. Your team should consider scalability during the design phase of any product. If a product or system is well received, it should be ready to scale. An example could be that an ecommerce website should handle at least 15,000 users during peak hours in the holiday season without affecting performance.
Scalability can relate to concurrent users, throughput, storage, or anything within the architecture of software that surpasses base specifications of the product. This is not a basic requirement of any product. But it gives flexibility to a product to appropriately react to growth and changing user demands.
Project planning without proper consideration of scalability could hinder your product from doing well. Scalability requirements are important to consider during the early stages of your product’s development.
Establishing strong scalability requirements can help your team define how to measure the success of your system’s ability to scale.
A well-defined scalability related NFR could say, “The system shall be scalable to support 10,000 concurrent users while maintaining the performance requirement of a 0.1 second response time.”
Survivability
Survivability is an operational aspect of a piece of software, a product, or a process.
It refers to the ability of a product or system to continue to operate and recover when experiencing a failure. This could be a failure caused by physical damage to hardware like a medical device or a digital attack on a system such as a DDoS attack.
When developed properly, survivability NFRs directly impact how teams assess the success of a physical product’s build quality and durability.
A well-defined software survivability NFR could say, “The system can prevent users from accessing a function of the system that is experiencing failure while still granting users access to unaffected functions.”
A well-defined hardware survivability NFR could say, “The product will still operate at 100% of its functional capacity if it is submerged in water up to 30 meters for 1 hour.”
Product marketing teams frequently use NFRs as major selling points. For example, watch companies and electronics manufacturers advertise the water-resistant rating of their products.
ii. Quantitative vs. Qualitative NFRs

NFRs tend to be qualitative as they are built to define attributes or qualities of a system. But to help teams measure the success of a system, you must first make a non-functional requirement measurable and sometimes quantitative.
An example of a non-functional requirement might be:
“The system should be scalable to handle enterprise expansion.”
Although the above is a valid non-functional requirement, it is not testable or easily measured. It may lead teams to build only qualitative NFRs without considering the application a quantitative measurement might have.
Adding quantitative values gives it a more definite measure of success for that requirement.
You could rephrase the above-mentioned example as: “The system should be scalable to 10,000 users within the next 2 years.”
Making it easier to measure and test allows you to better understand if a project is successful around the time it’s ending.
The way you structure a non-functional requirement should answer a few important questions:
- What are you measuring? Is it an application, a system, a project, or a process?
- What attributes are you measuring? Is it scalability, maintainability, security, or something else?
- What is your goal?
- What metrics are you using to determine success?
You can condense these answers into one statement:
- “The [insert answer to A] should be [insert answer to B] so that/to [insert answer to C]”
Building well-defined non-functional requirements can be tricky and their scope can be massive. But not having the right ones is also risky, as we have shown in this webinar.
iii. Measure Vs Metric
Not all NFRs need to be quantitative. In fact, qualitative and quantitative metrics can work together to meet your business goals. It is important to understand what the quantitative value represents and how that makes requirements more measurable. We have also shown some simple ways to reduce the time it takes to elicit them.
Requirements management metrics have a big effect on overall project success. But before you set up your metrics, it’s important to know the difference between measures and metrics.
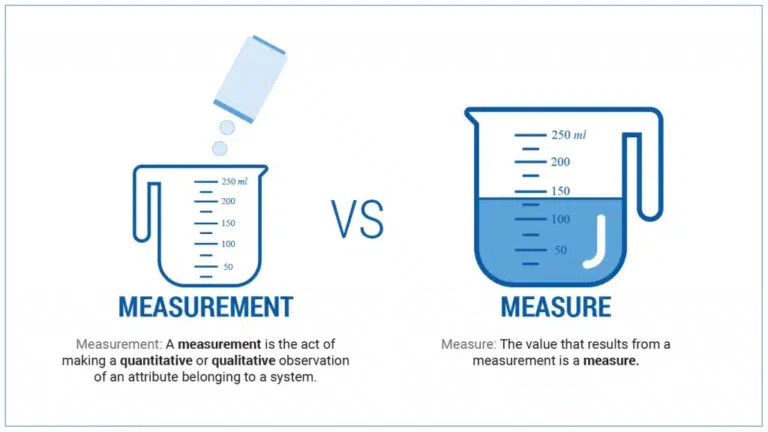
Measure
When building NFRs with quantitative values, you must give both a metric, whether they are measured qualitatively or quantitatively depends on the requirement itself.
A measurement is an observation that includes a value that represents a snapshot in time. In business, it is used to the amount or degree or something. Common measures include sales, revenue, cost, active daily users, etc.
A measure helps set the target value used to determine how close a system comes to fulfilling an NFR.
Metric
A metric is a value derived by comparing two different measures. In business, it is used to assess a specific business process and judge its performance. Common metrics include inventory turnover, customer lifetime value, and employee turnover.
When building NFR’s, we use metrics to evaluate what a particular value means in relation to our goal.
Now, let’s apply this knowledge to improve the NFRs that we create.
Well-defined quantitative and qualitative metrics are crucial for evaluating project success. This approach allows specific targets to make non-functional requirements (NFRs) more testable and measurable. For instance:
Stating “the system should be scalable to 10,000 users within the next 2 years” sets a clear, measurable target, as opposed to a more qualitative requirement like “allow multiple users.”
Even if some NFRs don’t include a direct metric, they can still be evaluated effectively. For example:
We can measure in two years whether a system supports an ecosystem of 10,000 users, making the requirement fully measurable and testable despite the lack of an ongoing metric.
Effectively defining NFRs allows for the testing and measuring of project success and software quality. However, with modern projects often having hundreds of NFRs, it’s essential to manage them efficiently.
This is typically achieved by categorizing them into three broad categories to streamline development and implementation. This categorization helps in focusing on specific aspects of system performance and ensuring each NFR is addressed appropriately.
3. Azure DevOps and Non-functional Requirements
Microsoft’s Azure DevOps is one of the world’s premiere Application Lifecycle Management tools today. In ADO, teams can leverage the platform’s flexibility to make requirements of any type.
NFRs are among the work item types you can create in Azure DevOps. You can configure non-functional requirements to house any variation of configurable fields, allowing them to contain any data important to your team. Within ADO, they are stored and treated no differently than any other requirement (epic, feature, user story, etc.).
Azure DevOps also supports the ability to configure your project backlog to easily show non-functional requirements where needed in your project.
But ADO falls short on several functionalities. Among others, there are no elicitation tools, no way to create and share documents, or do trace analysis.
4. The Role of Modern Requirements4DevOps

Modern Requirements4DevOps (MR4DevOps) helps you build non-functional requirements and offers several solutions to aid in the non-functional requirements management process. There is a tool for every stage of an NFRs lifecycle: Elicitation, Authoring, Document Creation, and Management.
i. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
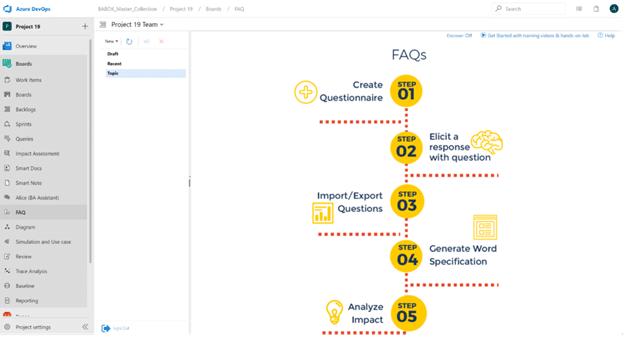
Effective elicitation questions help you find the right requirements for your project.
Building strong NFRs is based on asking the right questions. Due to their abstract nature, this isn’t always a simple task. MR4DevOps lets users elicit their NFRs with the FAQ module.
The FAQ module is a series of focused question lists grouped by system attribute and categorized by the three (3) aspects of the product:
- Operational
- Revisional
- Transitional
By answering questions from the list, you are authoring well-defined NFRs added to your Project Backlog. Users can modify existing lists by adding or removing questions and create their own custom FAQ lists. The FAQ module also contains question lists to elicit compliance and risk based NFRs for medical device development.
ii. Smart Docs
If documentation is part of your process, MR4DevOps’ Smart Docs gives you a single source of truth for your requirements documentation needs.
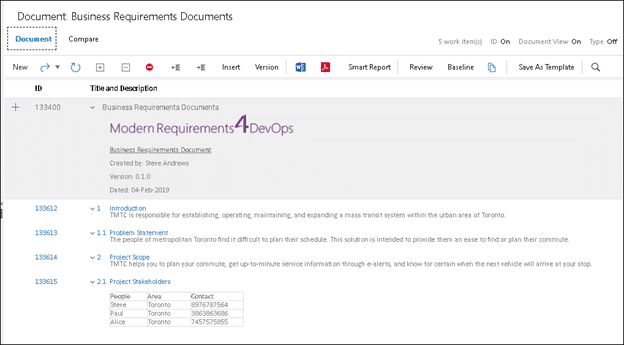
Smart Docs gives you an easy MS Word-like interface to handle NFRs effectively.
SmartDocs enables users to build non-functional requirements documents directly within Azure DevOps. You can insert existing NFRs directly from your backlog or author new ones on-the-fly while you build your Smart Doc. You can also build fully formatted documents using Smart Docs’ rich text editing functionality.
If your documentation process demands structure and consistency, you can employ reusable templates or tailor your specifications using the template designer. Additionally, a full version management feature is integrated directly into Smart Docs allowing users to quickly produce and output change documents.
iii. Reuse
Storing your well-defined NFR’s within a repository for later reuse is a best practice in requirements management. But, retrieving stored requirements and implementing them within a new project is a bulky process. MR4DevOps solves this problem with its highly efficient Reuse tool.
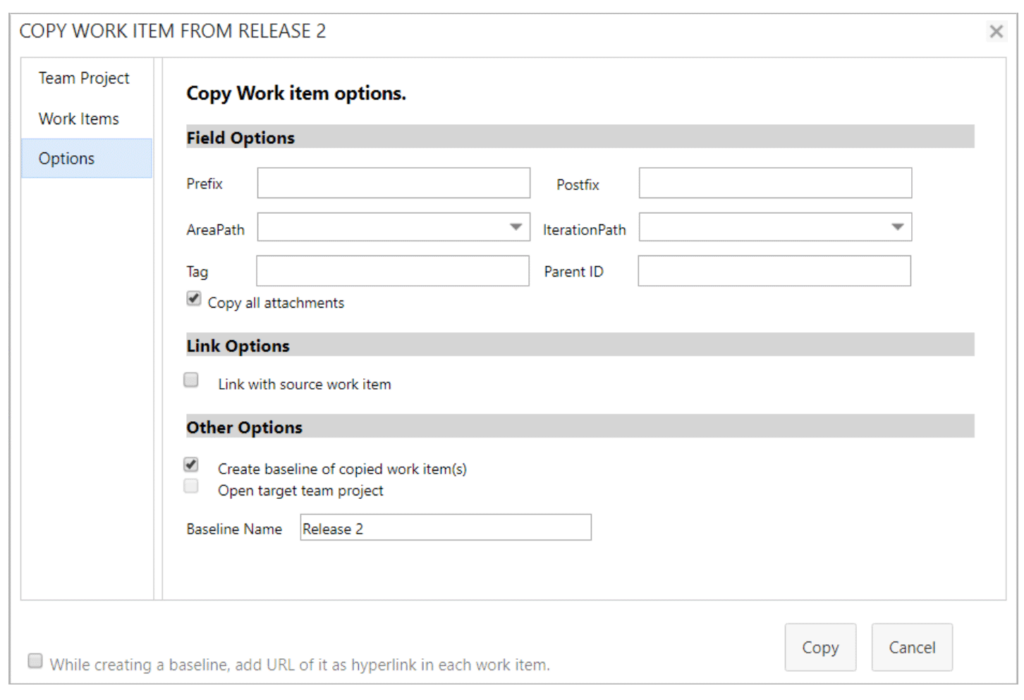
Storing your well-defined NFR’s within a repository for later reuse is a best practice in requirements management. But, retrieving stored requirements and implementing them within a new project is a bulky process. MR4DevOps solves this problem with its highly efficient Reuse tool.
Requirements reuse is key to increasing your employees’ productivity.
This tool allows users to copy existing work items from a project and insert them into new or existing projects within your collection or even across servers. You will never have to rebuild your well-defined NFRs again.
You can also manage and store your NFRs directly within Azure DevOps. MR4DevOps’ Reuse Work Item tool gives users freedom from managing external repositories, using outside applications, and the tedious copy and paste process.
iv. Trace Analysis
In terms of project management, accurate traceability of your non-functional requirements is one of the biggest challenges encountered by teams. Manually creating traceability matrices is a tedious, time-consuming, and error prone process. Projects typically evolve at a rate that renders them outdated. MR4DevOps’ Trace Analysis tool empowers users with the ability to create traceability matrices that show project coverage within seconds.
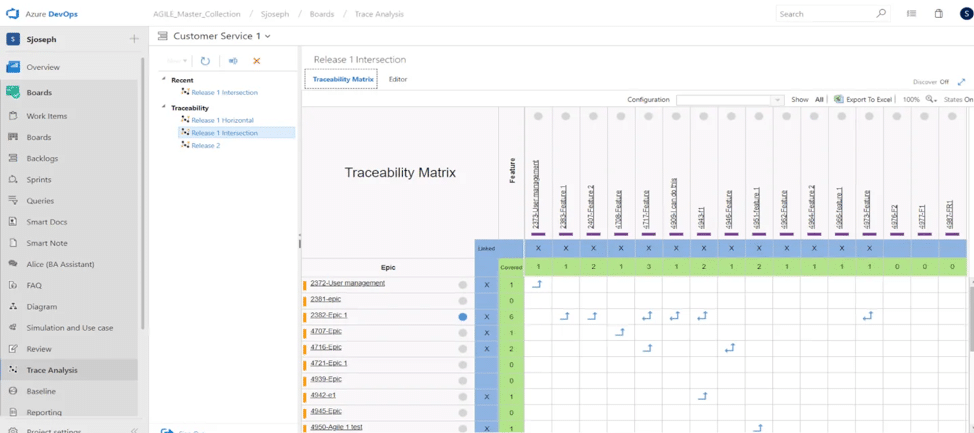
The Trace Analysis tool allows you to display and manage end-to-end traceability of your NFRs. Trace any relationship that exists between your project’s NFRs and any other requirement. Relationships between NFRs and other project requirements can also be created using the Trace Analysis tool.
MR4DevOps gives project managers an effective solution to one of the bulkiest processes in requirements management. Reclaim time lost to traceability. With MR4DevOps, traceability matrices can be built within seconds and are never out of date.
v. Generative AI
One way you could write higher quality NFRs is by using an AI requirements management tool. AI tools can streamline the process of writing non-functional requirements (NFRs) by assisting in requirements elicitation. Here’s how:
- Instant Elicitation: AI tools like Copilot4DevOps can generate NFRs at the touch of a button based on clicks or prompts, reducing the time and effort required for elicitation.
- Abundant Options: These tools can provide abundant options for NFRs, ensuring that all possible stakeholder needs are considered and captured, even those overlooked by skilled business analysts.
- Customization: Users can specify the output type they need, tailoring the AI-generated NFRs to match their project requirements precisely.
- Edit and Tailor: While AI can generate NFRs quickly, human intervention is essential for refining and tailoring them to meet stakeholders’ specific needs. Users can edit and modify AI-generated NFRs to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Analysis: Advanced AI tools can analyze the quality of the generated NFRs, grading them based on criteria such as clarity, completeness, and correctness. This analysis helps users further refine and polish the NFRs.
- Experimentation and Tracking: Users can experiment with different AI elicitation techniques and track the results to create a set of best practices tailored to their organization’s needs.
- NFR Document Generation: You can also generate high quality documents of non-functional requirements in a few clicks with a simple prompt.
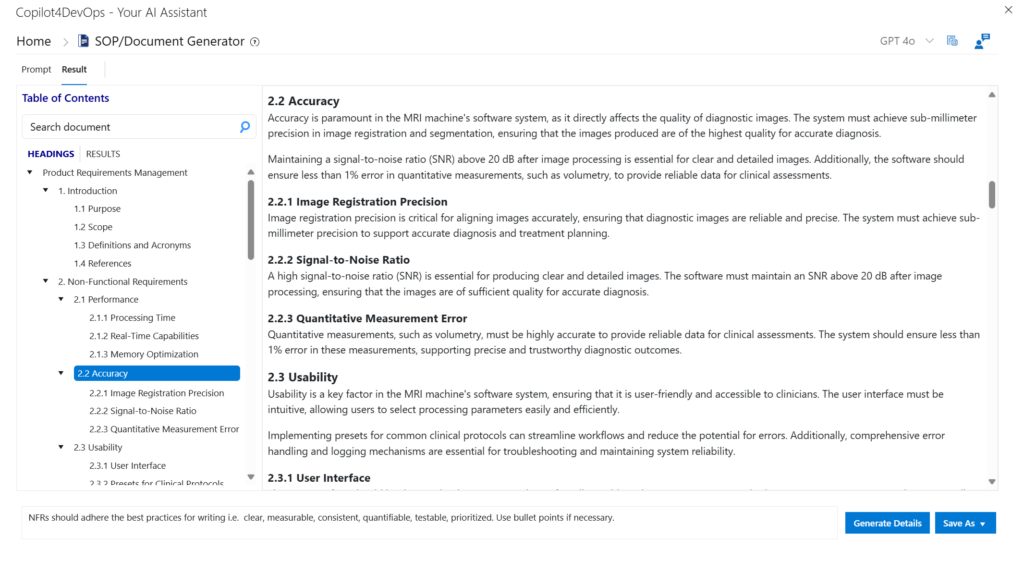
vi. Document Management System

Document Management System (DMS) is a tool that manages and organizes documents throughout their lifecycle, including those for non-functional requirements. It provides functionalities like version control, document comparison, and check-in/check-out mechanisms to streamline workflows. Integrated within Azure DevOps, it enhances collaboration, productivity, and reduces risks associated with document management.
5. Non-functional Requirements are Important
Non-functional requirements are an underappreciated but often critical part of application development. Done well, they have far greater depth and impact on your project than their functional counterparts. They can take your product, system, or service’s user experience to the next level.
MR4DevOps can help you elevate your NFR management capabilities with a set of tools that offer you support at every stage of your project. Contact us to find out how we can help you and your team with your goals.
Request a Demo!
- Schedule a demo with one of our trained product experts.
- Receive a personalized demo that mimics your team's process
- Engage our experts on topics such as workflow or best practices.

Reduce UAT Efforts
50% Reduction in UAT efforts

Proven Time Saving
80% time saving on creating Trace Analysis

Streamline Approvals
Significant reduction in approval delays

Increase Performance
50% requirements productivity improvement

Reduce
Rework
10-fold reduction in development rework
Simplify Compliance
40% reduction in compliance reporting efforts

